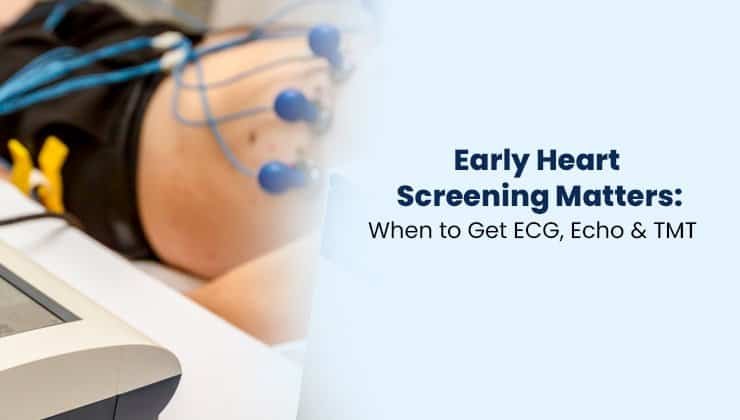
Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of illness and death worldwide. In today’s fast-paced lifestyle characterized by stress, sedentary habits, and unhealthy diets, protecting heart health has become important. Early heart screening plays a vital role, and it allows doctors to identify potential cardiovascular problems at an early stage and prevent future complications.
Read more to determine the importance of early heart screening, key diagnostic tests involved, who should get them, and how they contribute to long-term heart health and heart attack screening!
What Is Heart Screening and Why Is It Important?
Heart screening refers to a set of medical tests that may evaluate the health and functioning of the heart and blood vessels. It includes blood tests, an electrocardiogram, an echocardiogram, an exercise stress test, a coronary CT angiogram, and a cardiac MRI that may detect early signs of heart disease even before symptoms appear.
Heart screening is important as it helps in
- Early identification of hidden heart issues
- Lowers the risk of serious heart disease
- Helps determine the effectiveness of ongoing treatment
- Helps in tailoring personalized heart-healthy diet and care plans
Common Heart Conditions Detected Through Early Screening
Early heart screening plays an important role in identifying cardiovascular conditions at an early stage, allowing timely medical intervention and preventing complications. Common heart conditions detected include
- Coronary artery disease: Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries caused by plaque buildup that may lead to chest pain or heart attacks if left untreated.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms are detected through ECG, which may increase the risk of stroke or heart failure
- Hypertensive heart disease: Structural and functional changes in the heart caused by long-standing high blood pressure
- Heart valve disorders: Problems, including valve narrowing or leakage, that may affect blood flow through the heart
- Cardiomyopathy: Weakening or thickening of the heart muscle that may reduce the heart’s pumping efficiency.
Detecting these conditions early helps improve treatment outcomes and supports long-term heart health.
Understanding the Key Heart Screening Tests
What Is an ECG (Electrocardiogram)?
An ECG is a simple, non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart using small electrodes placed on the chest, arms, and legs. It helps doctors detect abnormalities in heart rhythm and function before serious complications occur.
How does the ECG work?
An ECG works by detecting the electrical signals generated by your heart as it beats. Small electrodes are placed on your chest, arms, and legs, which pick up these signals and transmit them to an ECG machine. The ECG machine then records them as wave patterns, showing the heart rate, rhythm, and electrical activity.
What does it measure?
An ECG measures the heart’s electrical activity, including the timing and strength of each heartbeat. It records
- how fast your heart is beating (heart rate)
- how regularly it beats (heart rhythm)
- how signals travel through the heart chambers (electrical conduction)
- Signs of heart strain or damage
- Conditions detected by ECG
An ECG may help detect several heart-related conditions, including
- Arrhythmias or abnormal electrical conduction
- Poor blood flow to the heart muscle due to coronary artery disease
- Heart attacks
- Heart chambers enlargement
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Conduction abnormalities
- When should you need an ECG?
The healthcare professionals recommend an ECG when patients complain of
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Unexplained fatigue
- Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
- Syncope and cyanosis (/blue hands and feet)
- Monitoring after a heart attack or surgery.
What Is an Echocardiogram (Echo)?
An echocardiogram, also known as Echo is a non-invasive scan used to visualize the heart and nearby blood vessels. It helps doctors assess heart structure, function, and blood flow to identify potential abnormalities. It provides detailed insights that an ECG alone cannot.
How does Echo work?
An echo is a type of ultrasound scan that uses a small probe to send high-frequency sound waves into the body. These sound waves bounce off the heart and surrounding structures, creating echoes. The probe captures these echoes and converts them into moving images displayed on a monitor.
How does Echo evaluate heart structure and function?
Echo provides detailed images of the heart chambers, valves, walls, and blood flow, helping doctors evaluate:
- Pumping efficiency of the heart
- Valve structure and movements of the heart walls
- Thickness and movement of heart walls
- Blood flow through the heart and major vessels
- Conditions detected by the Echo
An echocardiogram may help detect
- Heart damage from a heart attack
- Heart failure, where the heart cannot pump enough blood
- Congenital heart disease, structural heart defects
- Problems with the heart valves
- Cardiomyopathy, where the heart walls become thickened or enlarged
- Endocarditis is an infection of the heart valves.
- Pericarditis is an inflammation or infection of the sac that surrounds the heart
- When should you need an Echo?
Doctors may recommend an Echo if you experience
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath, fatigue or swelling in the legs
- Fatigue or weakness
- Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
- Suspected heart valve problems or structural abnormalities
What Is a TMT (Treadmill Test)?
A treadmill test (TMT), also known as a cardiac stress test, evaluates how well the heart functions during physical activity. It involves walking on a treadmill while heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are continuously monitored to assess the heart’s response to exercise.
How does the treadmill test work?
During a treadmill test, electrodes are placed on the chest to record ECG activity, and a blood pressure cuff monitors pressure levels. You will be asked to walk on a treadmill, with the speed and incline gradually increased to place additional workload on the heart. You will be monitored throughout the test, and the doctor will stop the test immediately if any problem or discomfort occurs.
How does TMT evaluate heart performance during exercise?
TMT shows how effectively the heart pumps blood when demand increases. It helps identify exercise-induced changes in heart rhythm, blood pressure, and ECG patterns that may not be visible at rest, indicating reduced blood supply to the heart muscle.
Why is TMT important for detecting blocked arteries?
Blocked or narrowed coronary arteries may not cause symptoms at rest but may limit blood flow during exercise. TMT helps reveal these blockages by detecting ECG changes, abnormal heart rate responses, or symptoms, including chest pain that suggests reduced oxygen supply to the heart.
When should you get a TMT (Stress Test)?
A TMT is recommended if you experience
- Chest pain
- Breathlessness
- Unexplained fatigue during activity
- Have risk factors, including diabetes or hypertension
- Need evaluation for coronary artery disease
- Monitoring after heart treatment or surgery
How Often Should Heart Screening Be Done?
A healthcare professional may determine how often heart screening is required for the individual based on the risk factors, age, and overall health of the individuals. It is important for everyone to undergo their first heart screening by the age of 20. You may be required to start screenings at a younger age if you are predisposed to certain risk factors for heart disease and carry a family history of heart disease.
- Adults under 40 with low risk of developing heart disease: every 2-4 years or as advised by a doctor. Basic screening, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and family history assessment
- Adults over 40 or with risk factors: Annually or as recommended by the doctor.
- High-risk individuals may need frequent and detailed screenings based on medical advice.
Regular heart screening ensures early detection of problems and helps prevent complications.
Benefits of Early Heart Screening
Early heart screening offers several advantages for maintaining cardiovascular health:
- Early detection of heart problems: Identifies hidden or developing heart conditions before symptoms appear
- Prevention of serious complications: Reduces the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure.
- Personalized treatment plans: Helps doctors tailor medications, lifestyle changes, and diet for optimal heart health.
- Monitoring ongoing health: Tracks the effectiveness of treatments and lifestyle modifications.
Early screening enables timely intervention, improving long-term outcomes and overall quality of life.
When to Consult a Cardiologist Immediately
It is recommended to consult a cardiologist immediately if you experience
- Severe or persistent chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
- Fainting, dizziness, or sudden weakness
- Blue or cold extremities
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Unexplained fatigue or extreme tiredness.
Seeking prompt medical attention may prevent serious complications, including heart attacks, heart failure or life-threatening arrhythmias.
Conclusion
Regular heart screening tests, including ECG, Echo, and TMT, play an important role in detecting heart problems early, reducing complications, and preventing life-threatening cardiac events. Early detection with lifestyle changes and proper medical care may help in maintaining a healthy heart.
For comprehensive heart screening services, book your heart check-up with leading cardiologists at Heart360 Care for personalized care and expert guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Heart screening tests are painless and non-invasive. ECG and Echo do not cause any discomfort as they record heart activity and images. TMT involves monitored exercise and may cause mild, temporary fatigue, but otherwise is generally well tolerated.
ECG typically takes about 5-10 minutes to complete, while Echo may take 30-60 minutes as it captures detailed heart images. Treadmill test usually lasts around 10-15 minutes with additional time for preparation, monitoring, and recovery under medical supervision.
Yes, ECG, Echo, and TMT tests are safe and are widely used cardiac diagnostic procedures. These tests are non-invasive and performed under medical supervision. However, fewer tests may carry rare complications, including temporary discomfort during exercise for stress tests, or in rare instances of arrhythmias induced during testing.
Heart screening cannot directly prevent heart attacks, but it helps detect early heart problems and risk factors associated with heart disease. Early diagnosis allows timely medical treatment and lifestyle changes, which may significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and other serious cardiac complications over time.
No, you may not always need all three tests. An ECG checks the heart’s electrical rhythm, an Echo evaluates the heart structure and valves, and a TMT assesses heart performance during exercise. Your healthcare provider will recommend the right test or combination of tests based on your age, symptoms, medical history, and risk factors to assess heart health.