The Cox Maze IV procedure, also known as the maze procedure, is a type of heart surgery that treats atrial fibrillation or AFib. Atrial fibrillation refers to an irregular heart rhythm that starts in the upper chambers of your heart, known as the atria.
The procedure is named after an American cardiothoracic surgeon, James Cox, who first developed the Cox Maze procedure as an open-heart surgery performed to eliminate atrial fibrillation. The techniques were then altered over time by using the latest medical advances and techniques.
The Cox Maze procedure initially involved the surgeon making several incisions in a maze-like pattern on the right and left atria of the heart. When these incisions started healing, the resultant scar tissue caused the blockage of the abnormal electrical impulses.
The scar tissue thus created a barrier to prevent the abnormal electrical impulses from being conducted throughout the heart, while allowing the normal heart rhythm to still get through the maze.
The current Cox Maze IV procedure uses ablation instead of cuts and stitches to create the maze, which involves the use of heat or cold energy to create small scars in the heart.
The Cox Maze IV procedure is the most effective in restoring normal sinus rhythm and maintaining it in patients with Long Standing Persistent AFib.
Dr. Nikhil
The Coz Maze IV procedure helps the patient get back his / her normal heart rhythm, prevent blood clot formation, reduce the risk of stroke, and control the heart rate.
In this article, we will be discussing the important aspects of the Cox Maze IV procedure.
Procedure:
The Cox Maze IV procedure is the most recent advancement of the maze procedure and is usually performed under the effect of general anesthesia, which means the patient will be put to sleep before starting the procedure. This procedure is usually performed in one of the following ways:
1. Sternotomy method
- A six-to-eight-inch vertical cut is made down the sternum bone, where the right and left ribs come together.
- The patient is put on a cardiopulmonary bypass machine to regulate the lung and heart functions during the surgery.
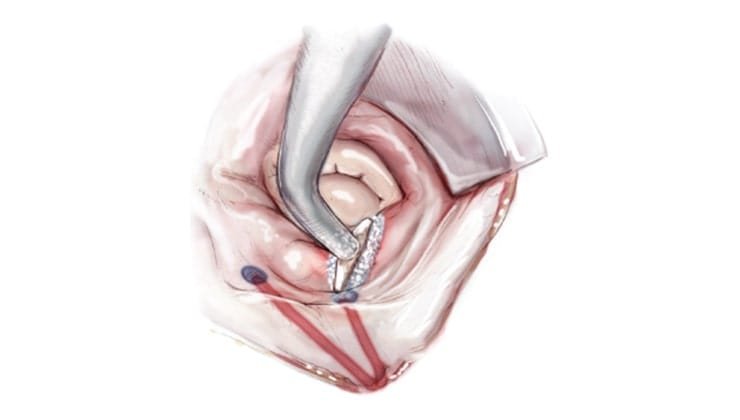
- A probe or clamp is used to apply surgical ablation energy source, such as radiofrequency or cryotherapy, to isolate the pulmonary veins (veins that bring the oxygen-rich blood back to the left atrium of the heart) so that the abnormal electrical signals don’t reach them.
- Ablation helps scar the tissue in the right and left atria in a specific maze pattern.
- The left atrial appendage (a tiny, ear-shaped tissue flap that is a common source of strokes and blood clots in people suffering from atrial fibrillation) is then removed or closed using staples, stitches, or a special device.
2. Thoracoscopic method
- A cut is first made between the ribs by the surgeon.
- The patient may or may not be put on a heart-lung bypass machine depending on the type of additional heart surgeries the patient is undergoing.
- The patient’s lung is deflated to allow the surgeon to perform the procedure using a minimally invasive technique.
- A tube with a camera on one end, known as an endoscope, and a port are then inserted by the surgeon between specific ribs.
- Ablations are completed in a manner similar to the sternotomy procedure.
- The left atrial appendage is then removed or closed by the surgeon.
Advantages:
The Cox Maze IV procedure has several benefits that include the following:
- Long-term relief for patients suffering from atrial fibrillation
- High success rate of 80 to 90%
- Reduces the risk of blood clot development and stroke
- Improved quality of life
Concomitant Procedure:
The Cox Maze IV procedure is an open-heart surgery that may require the patient to stay in the hospital for several days and approximately three to six weeks to recover completely.
Due to the invasiveness of the procedure, it is commonly performed simultaneously with other heart surgeries, like a valve repair or replacement surgery, or a coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG). This helps in addressing several heart problems at once.
When the Cox Maze IV procedure is performed simultaneously with another heart surgery, the procedure is known as concomitant ablation.
Post-Procedure Care:
The patient will be in the ICU or intensive care unit for one to two days after the surgery and then shifted to the normal recovery room, where the patient needs to stay for a couple of more days, depending on the different types of heart surgeries performed.
Generally, patients who have had a minimally invasive surgery will leave the hospital four to five days after the procedure, while others who have had more extensive surgeries may need to stay in the hospital for a week or more.
The doctor may recommend taking certain medications after the procedure, which may include the following:
- Blood-thinning medications or anticoagulants for at least three months after the procedure to prevent blood clot formation.
- Medications to control the abnormal heartbeats.
- Diuretics to reduce the amount of fluid the body retains.
Cardiac rehabilitation, lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and follow-up appointments with the surgeon are recommended after the surgery to ensure a smooth and quick recovery after the surgery.
Most patients can resume their normal activities three to six weeks after the procedure. It is important to follow the surgeon’s instructions carefully and take it slow during the recovery period before gradually resuming your normal daily life.
Though this is a commonly performed procedure in the western world, for various reasons it is not performed as indicated in India!
Dr. Nikhil