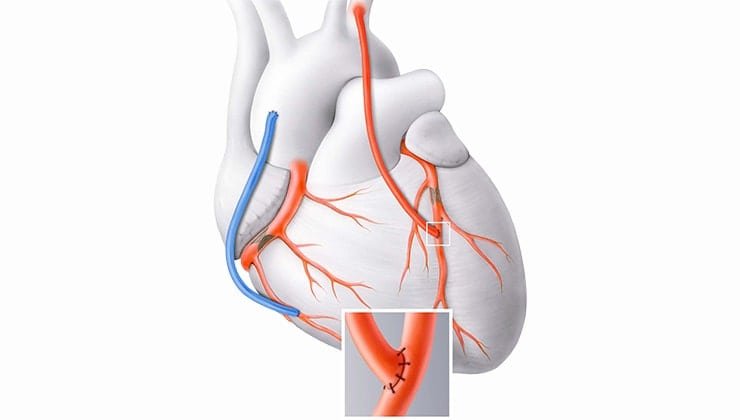
Bypass surgery, also known by the name heart bypass surgery or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a major operation performed for blocked arteries.
When the blood vessels narrow or are blocked by atherosclerosis (plaque deposition of cholesterol and fat), it cuts off oxygen-rich blood flow to the heart and leads to a heart attack. This condition is called Coronary Artery Disease (CAD).
In order to restore the normal pumping of blood, bypass surgery is performed. Here, blood vessels from other parts of your body are used to create a new pathway around the blocked artery to pass blood.
In short, in CABG, the new blood vessel bypasses the blocked arteries, improving the blood flow to heart muscles. Bypass surgery is one of the most commonly performed cardiac surgeries in India.
Who would benefit from bypass surgery?
Bypass surgery is often considered for people with severe blockage in the coronary artery that is irreparable by angioplasty or medications.
Bypass surgery is preferred typically when a patient has two or more major blocked vessels.
Dr.Nikhil
In case of a sudden heart attack, CABG may be performed as an emergency treatment. It helps ease the discomfort and symptoms of cardiac arrest, such as chest pain and blockages in the main left coronary artery.
How is bypass done?
Here’s a basic overview of creating new pathways around the blocked arteries to restore optimal blood flow.
Once the patient is under general anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest. This provides access to the heart and the blocked coronary arteries.
Next, a healthy blood vessel from the leg or the internal mammary artery is prepared for graft use.
The surgeon then creates a new pathway (bypass) around the blocked artery. This allows better blood flow to the heart. Multiple bypass grafts may be created depending on the number and location of blockages.
Dr.Nikhil says, “ Unlike what many patients think, we do not remove the blockages from the blood vessels; we just make pathways for blood to flow around the blocks.”
After the grafting is done, the incision in the chest is closed using sutures or staples. The patient will be monitored for stable vitals and pain management for several days. The hospital duration varies based on the overall health of the patient.
Types of Bypass Surgery
Traditional Bypass Surgery or On Pump:
In this open-heart surgery, also known as on-pump CABG, a heart-lung bypass machine is used, and the heart beating is paused temporarily. The machine takes over the functions of the heart and lungs and maintains blood flow when the grafting is being done.
Traditional bypass surgery is the Gold Standard for CABG!
Our chief cardiac surgeon, Dr. Nikhil
Off-Pump Bypass Surgery:
In this surgical approach, also called beating heart surgery, the surgeon operates on a beating heart without the help of a heart-lung machine. This reduces the complications associated with the bypass machine and allows for a quicker recovery.
MICS (Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery):
MICS, or Keyhole Cardiac Surgery, is performed by making small incisions in the chest through which special instruments with cameras are inserted. Compared to the previous types of bypass surgery, MICs have the benefits of reduced complications during and after the surgery, less pain, and reduced recovery time.
Robotic Assisted CABG:
This method is a type of MICS where robotic systems are used to assist surgeons during the procedure.
Recovery
A full recovery after bypass surgery generally takes 6-8 weeks. However, the recovery period can vary depending on the procedure’s complexity and the individual’s overall health.
Minimally invasive bypass surgery typically has a shorter recovery period of a few weeks. Cardiac rehabilitation programs like supervised exercise can help patients regain cardiac health.
Risks
Cardiac surgery is a major operation and carries certain risks and potential complications. Dr.Nikhil says, “Patients often ask about the risk of surgery but seldom realize that they are recommended surgery only because other options of taking medicines or stents were of higher risk.” Some of the potential risks are discussed below:
- There can be excessive bleeding during or after surgery. Our hospital performs blood transfusions or additional interventions to control such bleeding.
- There are chances of developing infections at the surgical site or within the chest cavity.
- Sometimes, blood clots can form in the legs that can travel to the lungs, causing complications like stroke.
- In some cases, cardiac surgery can trigger a heart attack because of the stress placed on the heart during the procedure.
- There can also be some risks associated with anesthesia.
Lifestyle Changes:
Making some adjustments to your lifestyle after a bypass surgery can impact your cardiac health significantly.
- Having a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium. This can help in controlling blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight.
- Opting to quit smoking can improve heart health and reduce the risk of complications after bypass surgery.
- Taking medications prescribed by the doctor for managing conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, etc, and preventing blood clots.
- Practicing deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and mild exercises to manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
- Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes obesity-related complications.
- Limiting alcohol intake helps to have a healthy heart.