Robotic cardiac surgery, or robot-assisted heart surgery, uses advanced robotic systems to perform cardiac operations accurately. In this type of surgery, a trained cardiac surgeon controls robotic arms that operate.
Unlike traditional open heart surgery, robotic cardiac surgery requires tiny incisions and is, hence, a minimally invasive surgical method. This approach helps perform complex heart surgeries and heart-related procedures, such as valve surgery, coronary artery bypass, cardiac tissue ablation, repair of heart defects, and removal of tumors, with minimal cuts.
How is Robotic Surgery done?
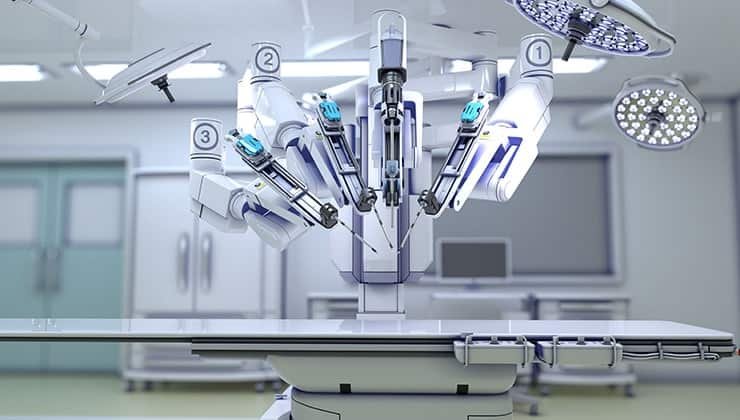
Robotic cardiac surgery is also known as da Vinci surgery, as the robotic system used in these surgeries is manufactured by a company called da Vinci. These robots have special arms equipped with specialized surgical tools and a high-definition camera.
A certified and trained surgeon in robotic surgery controls the operation from a console (similar to a computer control panel) that shows an enlarged, three-dimensional view of the heart during surgery.
There is a common misconception that the robot does the surgery in robotic cardiac surgery. In reality, it is the surgeon who is in control of the robot. The robot just translates the movements of the surgeon’s hands into the patient’s chest. So the surgeon is able to do the same heart surgery with smaller incisions.
Our chief cardiologist, Dr.Nikhil
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Patients undergoing robotic cardiac surgery experience several benefits compared to traditional open-heart procedures, such as:
- Faster healing due to smaller incisions
- Reduced bleeding
- Minimal damage to surrounding tissues
- Very less scarring
- Chances of infections are rare
- Shorter hospital stay
- Quicker recovery
Risks associated with Robotic surgery
Before undergoing any procedure, you should always discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks with your healthcare provider. Generally, robotic surgery poses very minimal complications in comparison to open heart surgery, as the procedure is minimally invasive. With minimal cuts and no larger opening of the chest, chances of bleeding and infections are drastically reduced.
However, like any surgery, there are some minor risks connected with robotic surgery, such as:
- There can be complications due to anesthesia, which can include breathing problems, nausea, and allergic reactions.
- While rare, there’s a small chance of injury to surrounding tissues or organs during the procedure.
- Although robotic systems are highly advanced, there’s a slight risk of technical issues or malfunctions during surgery.
- Robotic surgeries can sometimes take longer than traditional surgeries, which may increase the risk of complications.
- In some cases, such as if the surgeon encounters unexpected challenges or the patient’s condition is unsuitable for robotic surgery, the procedure may need to be converted to an open procedure.
Who Is A Good Candidate For Robotic Cardiac Surgery?
The decision to use robotic surgery for various heart conditions is based on several factors, including the size, location, and complexity of the problem. Some of the key parameters that influence the selection of candidates for robotic cardiac surgery are:
- Patients must be healthy overall, with controlled hypertension, diabetes, etc.
- Patients with a history of previous heart surgery may not be considered for robotic surgery.
- Patients with an obese body type may not be a good choice for robotic cardiac surgery due to the limitation of the length of the robotic arms.
- Patients should not have significant peripheral vascular disease because, for minimally invasive procedures, we need to connect them to a heart-lung machine using blood vessels in the groin and neck.
- The patient’s heart anatomy should be suitable for robotic-assisted procedures. This includes factors such as the size and position of the heart structures requiring intervention.