Cardiovascular or heart-related problems are known to be one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Advances in medical procedures and technology have helped to improve the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions.
Two such advanced techniques are angiography and angioplasty, that are used in the diagnosis and treatment of heart-related problems. While these procedures sound similar and even share similarities in terms of the equipment and procedure used, both these procedures are different and are used for different purposes.
We will be discussing the difference between angiography and angioplasty through this article.
What is Angiography?
An angiography is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that involves taking pictures of the blood vessels to check the blood flow through the blood vessels and detect the presence of any blockages.
The most common type of angiography is coronary angiography, which is used to check the blockages in the arteries that supply the heart.
Procedure of Angiography
The procedure for angiography involves the following steps:
- The surgeon may give sedatives to the patient to help the patient relax during the procedure, but the patient will stay awake during the procedure.
- Local anesthesia will be administered to numb the area where the surgeon will be making an incision or cut.
- A small incision or cut is then made over one of the arteries, near the groin or wrist area under the effect of local anesthesia.
- A thin tube, known as a catheter, will then be inserted into the artery.
- The catheter is slowly guided towards the heart region.
- The surgeon will then inject a special dye or contrast medium into the catheter to highlight the blood vessels in the X-rays.
- A series of X-rays will then be taken to have a look at the blood vessels as the contrast medium flows through them and check for any blockages or narrowing.
- The procedure is completed in 10 to 15 minutes and the patient is usually discharged within a couple of hours if no further treatment is needed.
Risks & Complications of Angiography
The complications associated with an angiography procedure may include the following:
- Soreness at the catheter insertion site
- Bruising at the catheter insertion site
- Blood vessel injury at the catheter insertion site
Other rare risks may include:
- Allergy to the dye used
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Kidney damage because of internal hemorrhage
- Stroke
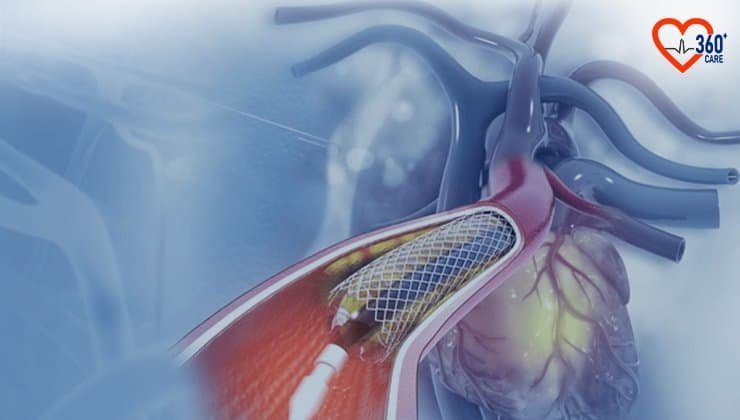
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive type of procedure performed to restore the normal function of the blocked or narrowed heart arteries by opening them using balloons or stents.
Coronary artery disease is a condition involving the accumulation of plaque, which is a sticky material composed of cholesterol, calcium, and other fatty substances, within the blood vessels (coronary arteries) of the heart.
Over a period, this plaque may lead to the blockage of the blood vessel due to which parts of the heart may not receive enough blood and lead to heart problems. An angioplasty is recommended to open the blocked arteries and restore blood flow to the heart.
Procedure of Angioplasty
The angioplasty procedure is done as follows:
- Just like angiography, the cardiac surgeon will first administer local anesthesia and make a tiny cut in the arm, groin, or wrist area.
- A catheter is now inserted through the incision made and guided to the heart.
- A contrast dye is then injected inside the coronary arteries to help highlight the heart and blood vessels in the X-rays.
- Once the blockages are identified, the surgeon will insert another catheter tube having a small, deflated balloon at one end.
- The surgeon will then inflate the balloon to help remove the deposited plaque, expand the blocked artery, and improve blood flow.
- In certain cases, the surgeon may insert a small mesh tube or stent into the artery to help in keeping it open. Medical coatings may be applied to some stents to stop the formation of blood clots.
- The deflated balloon is then removed.
Risks & Complications of Angioplasty
Angioplasty is generally considered to be a safe procedure but may be associated with some risks, like:
- Allergic reaction to the dye
- Blood vessel injury at the catheter insertion site
- Infection
- Triggering of blood clot formation in the treated artery
- Narrowing of the artery again, known as restenosis, if a stent is not used
- Prolonged and severe bleeding from the catheter insertion site
- Failure to open the blockage and the need to undergo emergency bypass surgery
Other rare complications associated with angioplasty may include:
- Arrhythmia or abnormal heart rhythm
- Coronary artery damage
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Kidney problems
What Is the Difference Between Angiography and Angioplasty?
The main angiography and angioplasty difference lies in their purpose. The various differences between these procedures include the following:
- Purpose
- Angiography is a diagnostic procedure recommended to visualize and identify the abnormalities or blockages in the blood vessels.
- Angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure performed to open up the narrowed or blocked blood vessels to improve blood flow in the heart.
- Procedure
- Angiography involves the insertion of a catheter into an artery and then injecting a contrast agent to visualize the blood vessels on the X-rays taken.
- Angioplasty involves the insertion of a catheter with a small balloon on the end into a blocked artery to open the blood vessel. This may be followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open.
- Duration
- Angiography usually takes anywhere between 15 minutes to 2 hours to complete, depending on the blockages or anomalies found.
- Angioplasty normally takes 20 minutes to 3 hours to complete, depending on the extent of the blockage present.
- Recovery Time
- The patient can usually go home a couple of hours after an angiography procedure. Mild pain or bruising may be present at the site of catheter insertion for a few days after the procedure.
- The patient can normally go home one to two days after an angioplasty procedure. Pain and bruising at the catheter insertion site will disappear in a few days. However, recovery will take much longer and each patient recovers at his or her own pace. Strenuous activities need to be avoided during the recovery period.
Is an Angiography Necessary Before an Angioplasty?
An angiography is usually ordered before undergoing an angioplasty to view the arteries of the heart. The images obtained in an angiogram help in the detection of blockages in the heart arteries.
Angioplasty is one of the commonly recommended treatment options offered when there are blockages found in the heart arteries.
In fact, an angiography procedure may progress to an angioplasty procedure during the same visit if blockages are found.
Angioplasty Vs Angiography: When Does the Doctor Advise?
The doctor may recommend undergoing an angiography in the following situations:
- Chest pain or angina
- Problems with the blood vessels of the heart
- Chest, arm, jaw, or neck pain that does not respond to other diagnostic procedures like ECG (electrocardiogram)
- Congenital heart defect
- Abnormal stress or treadmill test results
- Chest injury
- Heart valve diseases need surgery
An angioplasty may be recommended by the doctor in the following cases:
- Angiography shows significant narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries
- Chest pain that worsens
- Immediate restoration of blood flow for treating a heart attack
Cost of Angioplasty Vs Angiography
The cost of angiography and angioplasty varies depending on many factors like the hospital chosen, expertise of the cardiac surgeon, location of the hospital, whether the hospital is private or government, type or procedure done, the complexity of the case, and additional procedures or tests that may be done.
The approximate cost of angiography in India varies between INR 20,000 to INR 60,000, whereas the cost of angioplasty in India can vary from INR 70,000 to INR 2,50,000.
Conclusion
Angiography refers to a diagnostic procedure performed to diagnose blockages or narrowing of arteries, whereas angioplasty is a therapeutic intervention performed to open the narrowed or blocked arteries to restore blood flow to the heart.If you are suffering from heart problems and want more information about angioplasty vs angiography, you should contact Dr. Nikhil P.J.Theckumparampil, Heart Specialist & Cardiac Surgeon at Heart360 Care in Chennai, for a thorough heart evaluation and undergo successful heart-related procedures like angiography and angioplasty.